Plans supporting this feature: Professional Business Enterprise
Self-registration lets users create their own reader accounts without needing an invitation from a project team member. To enable self-registration, share your knowledge base URL with users, allowing them to create their accounts independently.
Once registered, readers are automatically added to the Readers list. Project members with access to User & permissions settings can edit or remove these readers as needed.
NOTE
The Readers self-registration feature is available only if your Document360 project’s Reader access is set to Private or Mixed.
Self-register on a Knowledge base site
To self-register on a Knowledge base site:
Go to your Knowledge base site.
Click Sign up at the bottom of the login screen.
.png)
Enter your First name, Last name, and Email.
Click Sign up.
You will get a confirmation message saying, ‘Account created successfully’.
You will receive an invitation email. Once verified, you can set a password and log in to the knowledge base site.
NOTE
An email only needs to be verified once. After that, it can be used across multiple projects.
Overview of Reader self-registration
To access the reader self-registration page:
Navigate to Settings () > Users & permissions in the left navigation bar in the Knowledge base portal.
In the left navigation pane, navigate to Readers & groups > Readers.
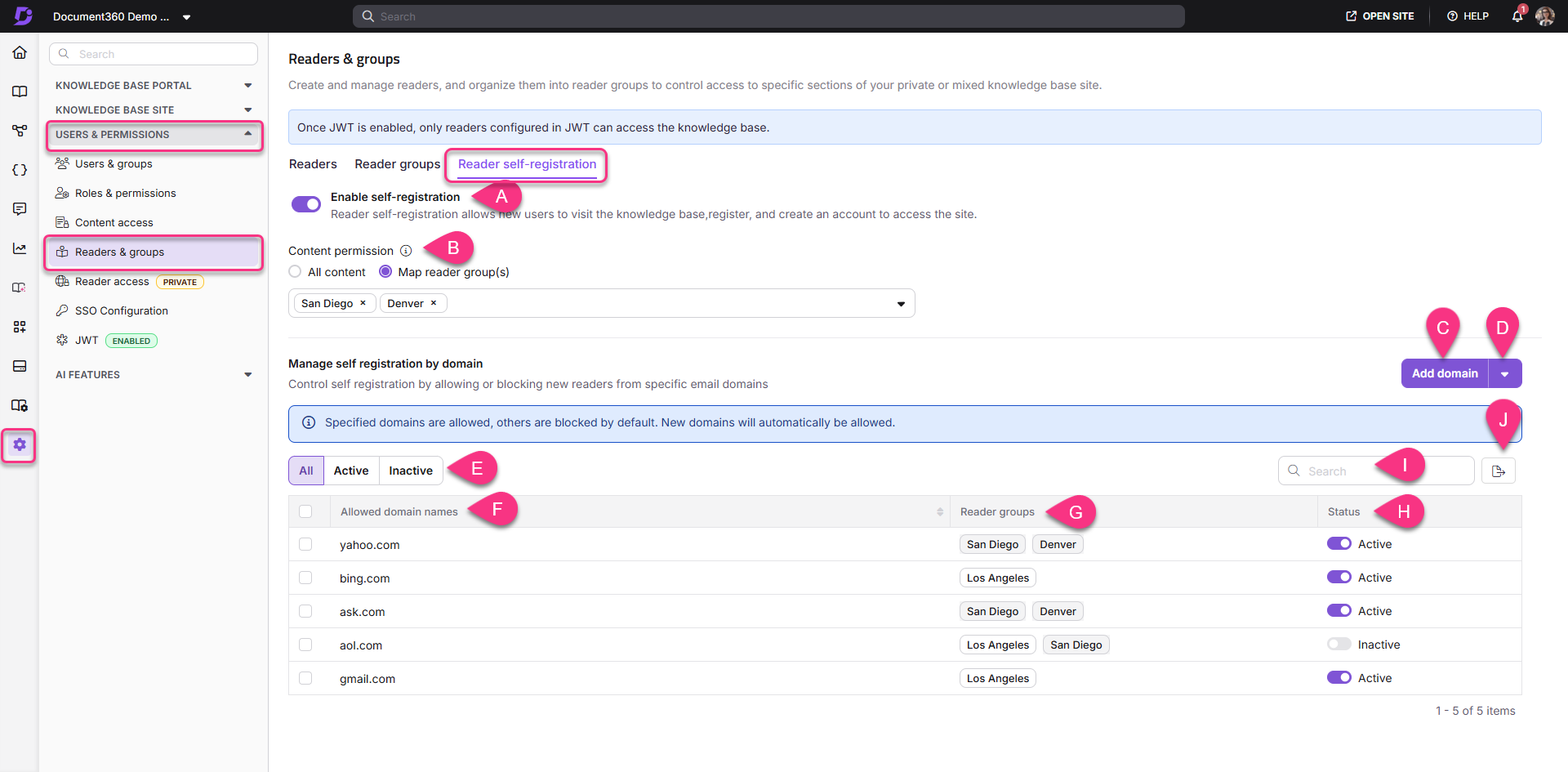
Key elements of the Reader self-registration page:
Enable reader self-registration: Turn on the toggle to allow readers to self-register.
NOTE
To disable reader self-registration, follow these steps:
In the Reader self-registration page, turn off the Enable reader self-registration toggle.
Click Disable in the Disable reader self-registration panel.
If the Enable reader self-registration toggle is turned off, readers cannot register themselves.
Content permission: Select the desired content permissions:
All content: Readers can access all Knowledge base content.
Map reader group(s): The content access permissions of the selected reader group(s) will apply to the domains.
Add domain: Add a new domain for domain restriction.
Import domain: Import multiple domains for domain restrictions.
Filter options: View domains filtered as All, Active, or Inactive.
All: Displays all allowed or blocked domains.
Active: Lists only active domains.
Inactive: Lists only inactive domains.
Allowed/Blocked domains: Displays all domains for the project. Click the column header to sort the list alphabetically; click it again to reverse the order.
Reader groups: Shows reader groups mapped to domains.
Status: Indicates whether domains are Active or Inactive.
Search: Search for specific domain names.
Export: Export the list of domains as a CSV file.
Adding a domain restriction
To add a domain restriction, follow the steps below:
Navigate to Settings () in the left navigation bar in the Knowledge base portal.
In the left navigation pane, navigate to Users & permissions > Readers & groups > Readers.
Turn on the Enable reader self-registration toggle to allow readers to self-register.
Click Add domain to add a new domain.
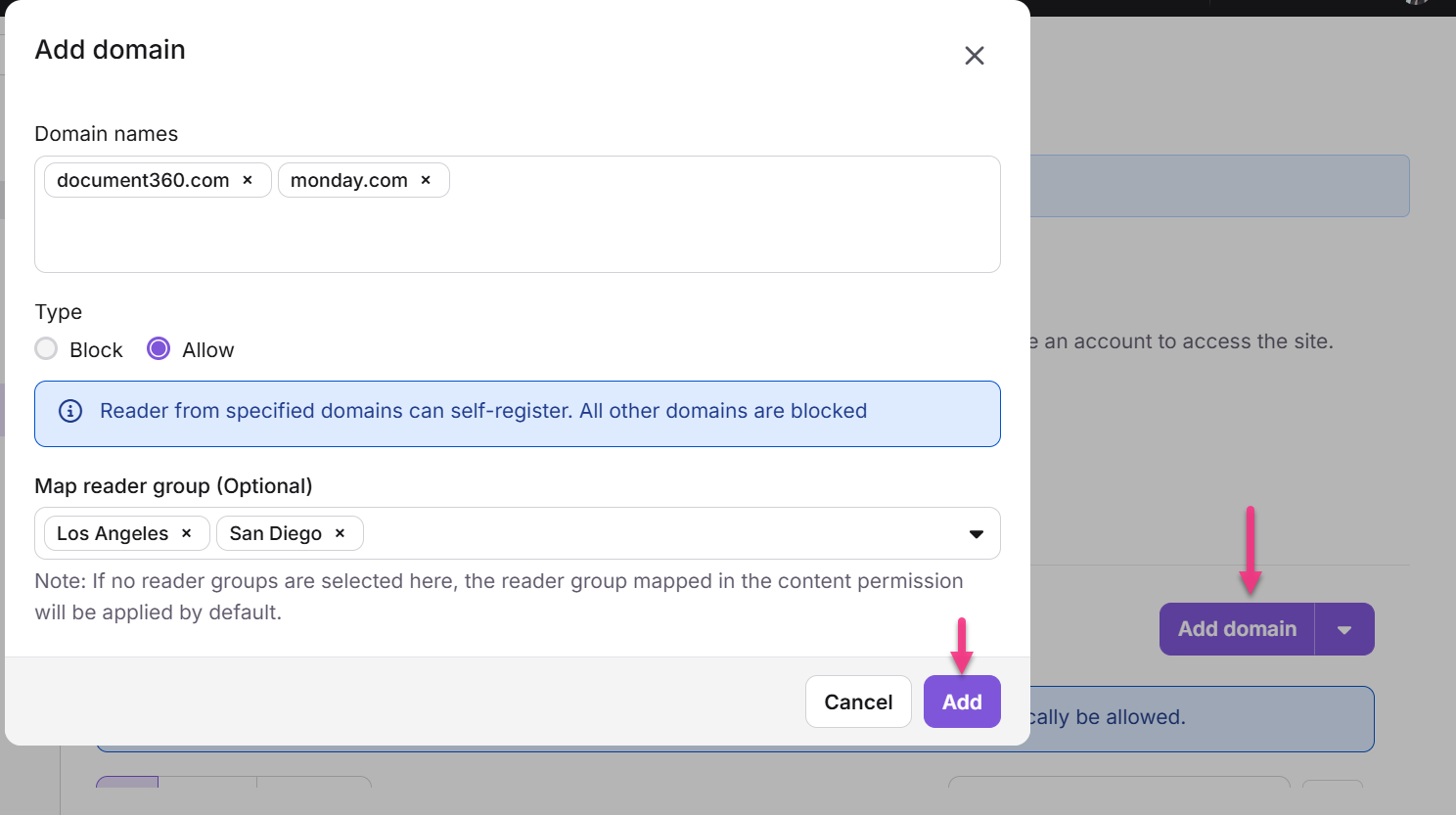
The Add domain panel will appear.
Enter the desired domain names (e.g., everything after the @ symbol, like
@genericmail.comor@randomdomain.com) and press Enter.To remove a selected reader group, click the icon to clear the entries in the line.
NOTE
You can add up to five domain names, separated by commas.
Select the restriction type:
Block: Readers from the specified domains are restricted from self-registering, while others can self-register.
Allow: Readers from specified domains can self-register. All other domains are blocked.
If selecting Allow, optionally map the domain to a reader group.
NOTE
If no reader groups are selected, the reader group mapped in the content permission will be applied by default.
If both the Map reader group(s) in the content permission and the domain-specific reader group(s) are enabled, the domain-specific settings will take precedence over the default reader groups.
Click Add to save the restriction.
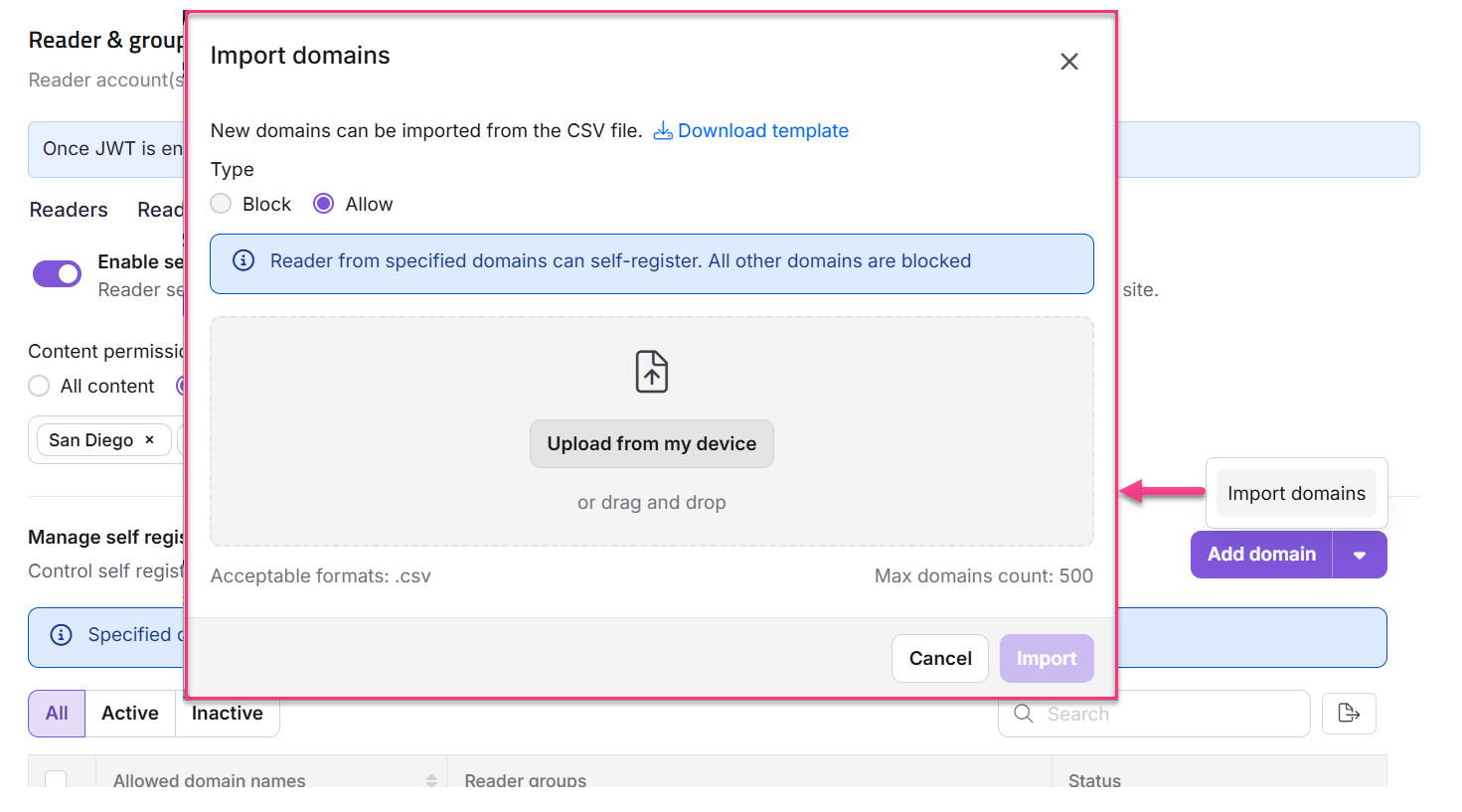
Importing multiple domains
To import multiple domains in readers self-registration page, follow the steps below:
Navigate to Settings () > Users & permissions in the left navigation bar in the Knowledge base portal.
In the left navigation pane, navigate to Readers & groups > Readers.
Click the dropdown next to Add domain and select Import domains.
The Import domains panel will appear.
Click Download template to get the sample CSV template.
Upload the CSV file using one of the following methods:
a. Upload from my device: Select the CSV file from your local file explorer.
b. Drag and drop: Simply drag and drop the CSV file into the designated area.
NOTE
You can import up to 500 domains at once.
A validation summary will display:
Valid Domains: Number of valid entries.
Invalid Domains: Number of invalid entries (click the Download () icon to view details).
Select the restriction type: Block or Allow.
Click Import.
Editing and deleting a Domain restriction
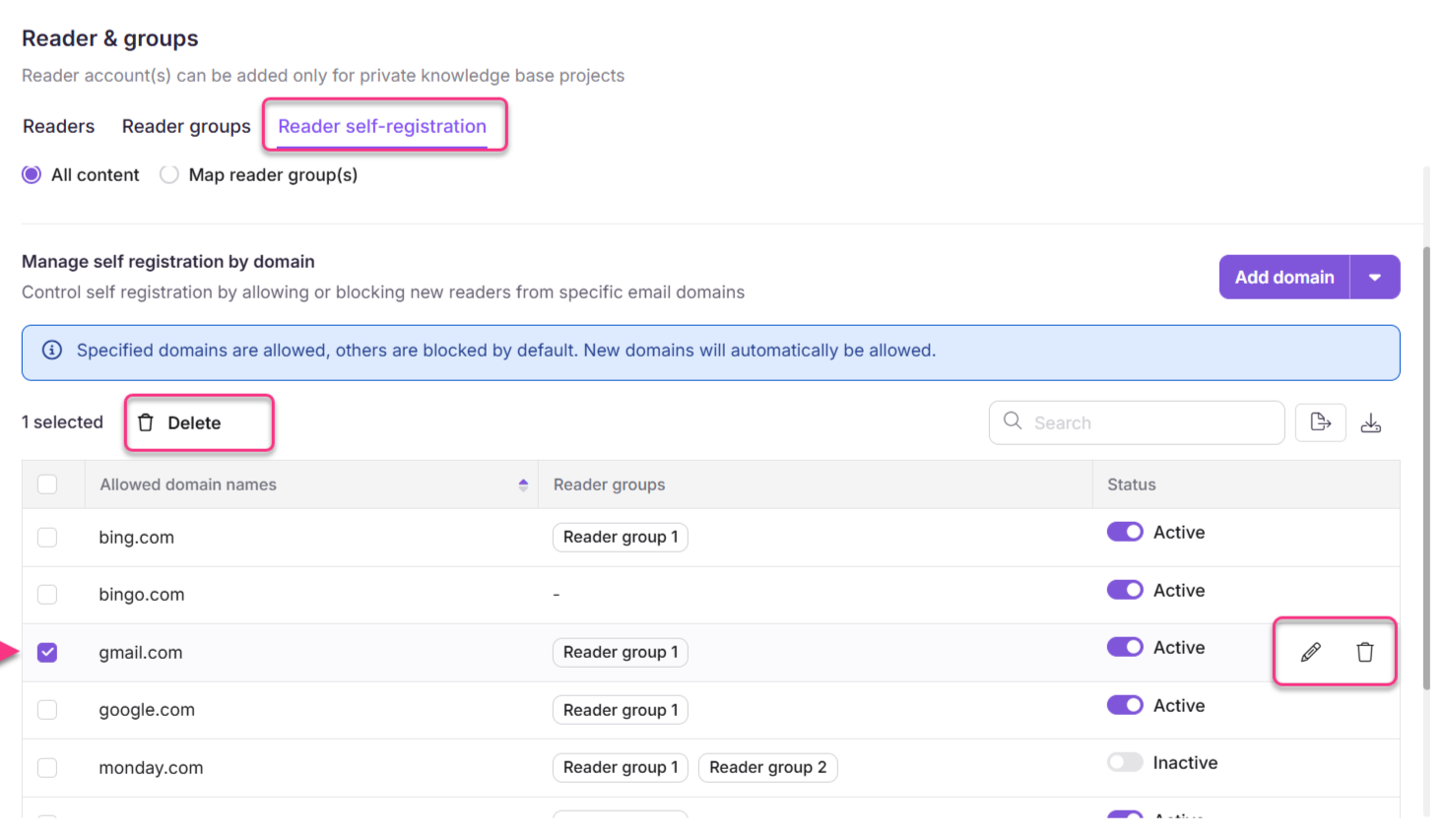
To edit a domain restriction:
Hover over the desired domain name on the Reader self-registration page.
Click the Edit () icon to modify the domain restriction configuration.
To delete a domain restriction:
Hover over the desired domain name and click the Delete () icon.
Alternatively, select the checkbox next to the domain name, and then click Delete () at the top of the list.
Understanding domain restriction
Domain restrictions determine whether readers from specific domains can self-register, based on the selected restriction type and the domain's status. This feature lets you control who can register on your knowledge base by email domain.
Restriction type | Domain status | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
Allow | Active | Readers from the domain can self-register. | A company adds |
Allow | Inactive | Readers from the domain cannot self-register. | The domain |
Block | Active | Readers from the domain cannot self-register. | A general email domain like |
Block | Inactive | Readers from the domain can self-register. | The domain |
FAQ
What happens if no default reader group is selected?
If no default reader group is selected, self-registered readers will have unrestricted access to the entire knowledge base, without any group-specific restrictions.
What access do readers with multiple group memberships get?
When a reader is part of multiple groups, the highest level of access for each content item is granted.
For instance, if a reader belongs to Group A (which has access to all languages in workspace 'V1') and Group B (which has access to only English in 'V1'), the reader will receive access to all languages in workspace 'V1'.
Does individual content access override reader group access?
No, individual content access does not override group access. The reader always receives the highest privilege from both individual and group settings.
For example, if a reader is individually set to access only English in workspace 'V2' but is also part of a group that has access to all languages in 'V2', the reader will have access to all languages in 'V2'.
How is reader access prioritized?
Access is determined by the highest privilege assigned at each content level. Readers only gain access to the content they have been specifically granted.
Why is self-registration not working for my project?
Self-registration does not function as expected when SSO (Single Sign-On) is enabled because SSO bypasses the Document360 login page, where self-registration typically occurs. Self-registration with domain configuration is designed for use on the Document360 login page only.