If your knowledge base is private or restricted to specific users, you can use JWT (JSON Web Tokens) to securely control access to the embedded Document360 widget. This setup ensures that only authenticated users can view articles through the widget, without requiring them to sign in separately.
With JWT authentication, your system handles login and token generation. The widget then uses that token to fetch content based on each user’s access level.
In this article, you'll learn:
How JWT authentication works for widgets
How to configure JWT settings in the Document360 portal
How to set up your backend to generate and return secure tokens
How JWT authentication for widgets works
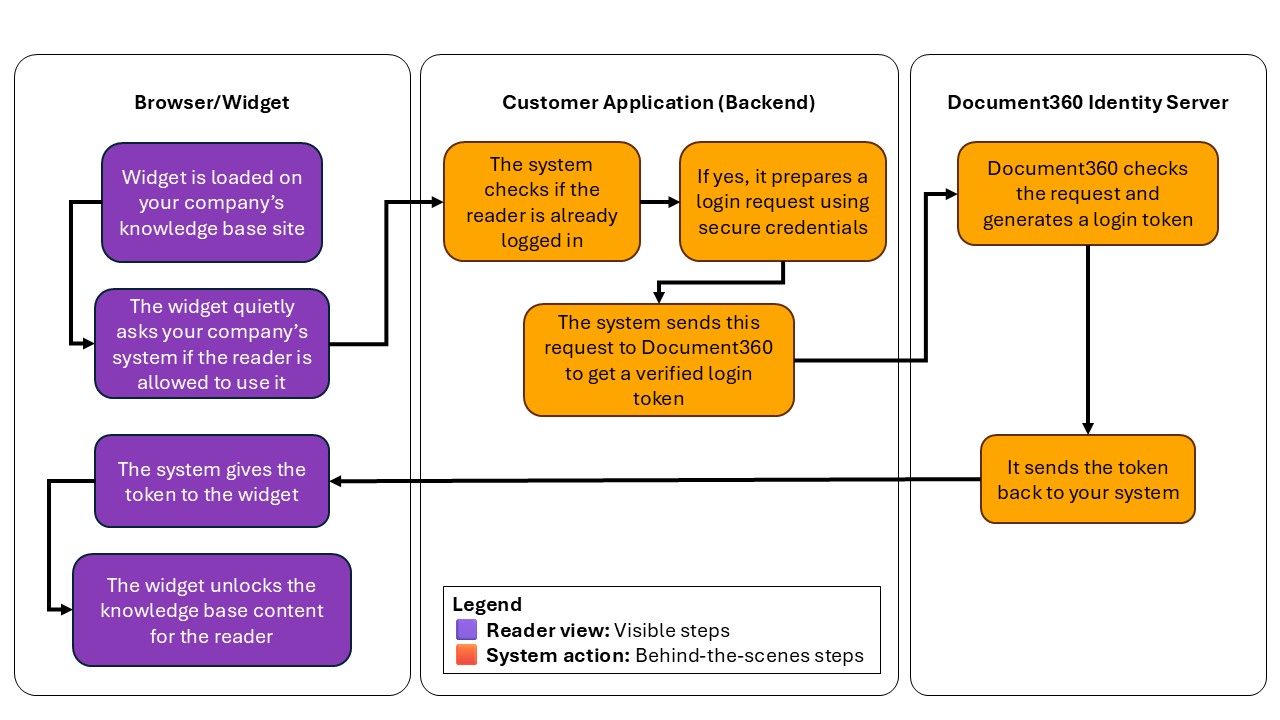
Visual overview of the authentication process
This flow diagram shows what happens when a user loads a widget on your website. The Document360 widget communicates with your system to get a secure token before displaying content.
Sequence diagram of the authentication process
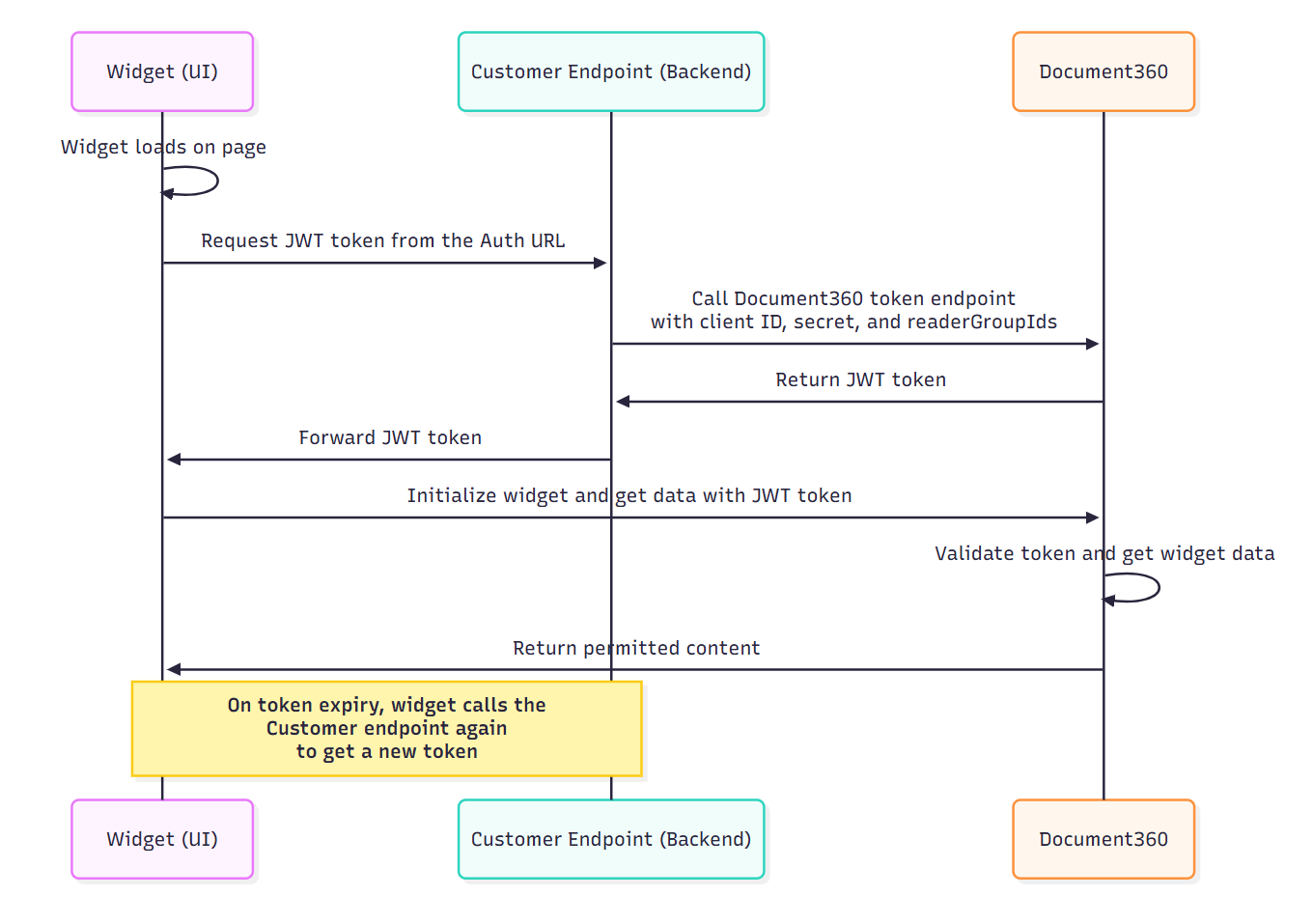
This sequence diagram outlines the technical flow between the user’s browser, your backend, and Document360’s identity server to generate and validate the JWT token.
The steps below explain the complete JWT authentication flow:
User visits your website, where the Document360 widget is embedded.
The widget sends a silent request to your authentication endpoint (token endpoint) configured in the widget settings.
Your backend sends a request to Document360 with the required credentials (client ID, client secret) and reader details.
Document360 validates the request and returns a signed JWT to your backend.
Your backend sends the token back to the widget.
The widget uses this token to fetch and display articles that the reader has access to.
When the token expires, the widget automatically requests a new one (if configured to do so).
NOTE
The above flow happens behind the scenes. Readers never see a login screen for the widget.
Enable and configure JWT for the widget
You can implement an authentication configuration for the widget using JWT, ensuring a secure environment for private and mixed projects.
Navigate to Connections () > Knowledge base widget in the left navigation bar.
The list of widgets will appear.
Hover over the desired widget you want to configure and click the Edit () icon.
In the Configure & connect tab, navigate to the JWT accordion and turn on the JWT Enable toggle.
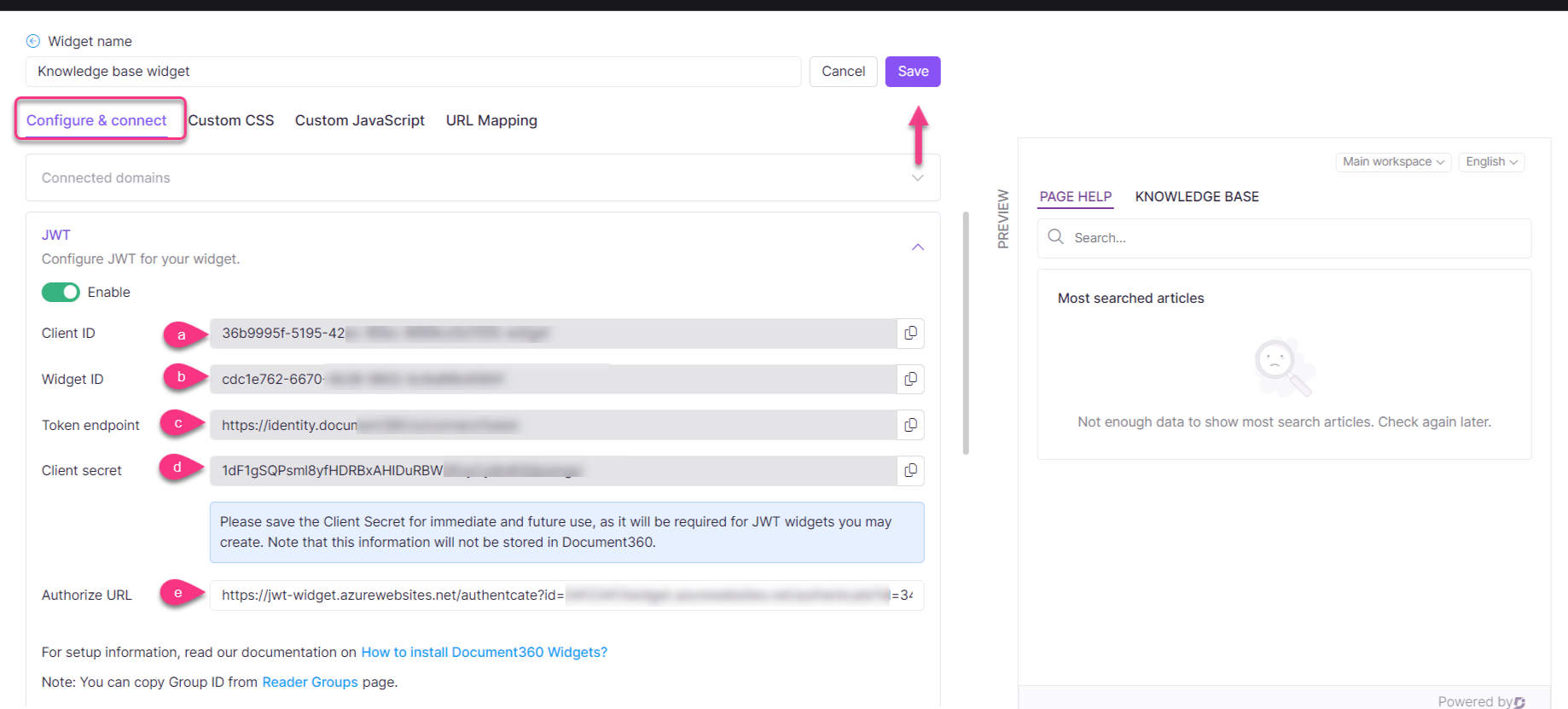
Client ID: The client ID will be your project’s ID.
Widget ID: Since multiple widgets may exist, a Widget ID is provided for their unique purposes.
Token endpoint: A token endpoint is an HTTP endpoint that allows you to obtain an access token given an authorization code.
Client secret: Click Regenerate to generate the client secret. You need to save this for future purposes, and the same client secret will apply to all widgets in the future.
NOTE
The Client secret will be required for JWT widgets you may create. Note that this information will not be stored in Document360.
e. Authorize URL: Paste the authorized URL from your knowledge base widget webpage.
Click Save to apply changes.
Embed the authorized URL within your code and paste it into the script section on your webpage. This will implement a secure, authenticated widget that prevents unauthorized third-party access.
Implementing the auth endpoint
After configuring JWT in the portal, you’ll need to set up an authentication endpoint in your backend application. This endpoint receives a request from the widget and returns a valid token in response.
The example below shows how to implement the endpoint in C#.
/// <summary>
/// Endpoint to authenticate a user, generate a JWT token from Document360,
/// and return it to the widget.
/// </summary>
[HttpGet]
[Route("authenticate")]
public async Task<IActionResult> WidgetAuthentication(string id)
{
// Ensure the user is authenticated in your application
if (!HttpContext.User.Identity.IsAuthenticated)
{
return Unauthorized(new { message = "User is not authenticated." });
}
// Define configuration values
var clientData = new ClientDetails
{
ClientId = "{Client ID}", // Replace with your project’s client ID
Secret = "{Client secret}", // Replace with your generated client secret
TokenEndpoint = "{Token endpoint}", // Replace with the token endpoint URL from Document360
WidgetId = "{Widget ID}", // Replace with your widget ID
SecurityGroupIds = "group1,group2", // Replace with comma-separated reader group IDs
TokenValidity = 15 // Token validity in minutes (5–1440)
};
// Return 404 if configuration is missing
if (clientData == null)
{
return NotFound(new { message = "Client configuration not found." });
}
// Convert the comma-separated reader group IDs into a list
List<string> readerGroupIds = null;
if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(clientData.SecurityGroupIds))
{
readerGroupIds = clientData.SecurityGroupIds
.Split(',')
.Select(c => c.Trim())
.ToList();
}
// Prepare the payload with user and configuration details
var payload = new
{
username = "{Username}", // Replace with actual user data if available
firstName = "{First name}",
lastName = "{Last name}",
emailId = "{Email address}",
readerGroupIds = readerGroupIds,
tokenValidity = clientData.TokenValidity,
widgetId = clientData.WidgetId,
projectId = clientData.ClientId
};
var payloadString = JsonConvert.SerializeObject(payload);
try
{
// Send request to Document360 token endpoint
var result = await client.RequestTokenAsync(new TokenRequest
{
Address = clientData.TokenEndpoint,
ClientId = clientData.ClientId,
ClientSecret = clientData.Secret,
GrantType = "Widget",
Parameters =
{
{ "payload", payloadString },
{ "id", clientData.ClientId }
}
});
// Return the access token to the widget
return Ok(new
{
accessToken = result.AccessToken,
expiresIn = result.ExpiresIn
});
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
// Handle unexpected errors (optional)
return StatusCode(500, new
{
message = "Failed to generate token.",
details = ex.Message
});
}
}NOTE
The
tokenValidityvalue is set in minutes. It must be between 5 minutes (300 seconds) and 1440 minutes (86,400 seconds). If you enter a value outside this range, the system automatically adjusts it to the nearest valid value. For example, if you settokenValidityto 1 minute (60 seconds), the system increases it to the minimum allowed value of 5 minutes (300 seconds).The widget requires at least one valid reader group ID to render content. Include these as a comma-separated list in the
readerGroupIdsparameter of the JWT payload.
Test your JWT widget configuration using Postman
After setting up JWT in the Document360 portal and implementing your backend authentication endpoint, you can use Postman to confirm that your configuration works as expected.
This test simulates what the widget does: it sends a request to your backend to fetch a valid JWT.
Set up the test in Postman
Launch Postman.
Select + New tab or click New > HTTP request.
Set the method to POST.
In the request URL field, enter the full URL of your backend endpoint.
Example:
https://yourdomain.com/authenticateGo to the Authorization tab.
Under Type, select Basic Auth.
Enter the following credentials:
Username: Your Client ID from the Document360 portal.
Password: Your Client Secret (generated when you created the JWT).
Next, to set the request body, go to the Body tab.
Select raw.
Choose JSON from the dropdown on the right.
Paste the following example JSON into the body:
{ "username": "john.doe", "firstName": "John", "lastName": "Doe", "emailId": "john.doe@example.com", "readerGroupIds": ["group1", "group2"], "tokenValidity": 15, "widgetId": "your-widget-id", "projectId": "your-project-id" }Replace the values with actual data from your app and Document360 configuration.
If the request is successful, you’ll receive a JSON response like the following:
{
"accessToken": "eyJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiIsInR5cCI6IkpXVCJ9...",
"expiresIn": 900
}accessToken: This is the signed JWT that the widget will use to authorize the reader.expiresIn: Token validity in seconds (15 minutes = 900 seconds).
After sending the request, check that the response status is 200 OK, indicating a successful request. The response body should contain a valid accessToken, which is the signed JWT used by the widget. Additionally, confirm that the expiresIn value matches the expected token validity duration in seconds (for example, 900 seconds for 15 minutes).
If all these values appear correctly, your JWT setup is working as intended.