Plans supporting this feature: Enterprise
What is a JWT?
A JSON Web Token (JWT) is an encrypted token format that securely transfers data, such as credentials (authentication and authorization), between two applications. JWT is specifically used to authenticate reader logins in Document360. Click here to read about JWT.
Enterprise SSO using JWT in Document360
Document360 supports JWT (JSON Web Token) as one of its SSO (Single Sign-On) methods, primarily used for authenticating reader logins. JWT provides a secure way to transfer authentication and authorization data between your application and the Document360 knowledge base.
Document360 uses an approach similar to PKCE (Proof Key for Code Exchange, a secure OAuth method) to generate the JWT token.
Choosing the right SSO method: JWT vs SAML vs OpenID
Document360 supports three SSO options for reader authentication: JWT, SAML, and OpenID Connect. Choosing the right method depends on how you manage users, what infrastructure you already have, and how much control you need over the login process.
The table below compares JWT against the other options:
Feature | JWT | SAML / OpenID |
|---|---|---|
Reader management | Readers are authenticated from your own application. You don’t need to create or manage reader accounts manually in the Document360 portal. | Readers are managed through your organization’s identity provider (IdP) like Okta, Azure AD, or Google Workspace. |
Login destination | JWT logins always redirect to the knowledge base site. Even if the user is a team member, they cannot access the Document360 portal using JWT. | Can support both reader and team logins, depending on configuration. |
When to use | Ideal if you don’t have an IdP, or prefer to manage authentication in your own app. | Recommended if your organization already uses an IdP and wants centralized authentication and access control. |
User registration flow | You control the login and user provisioning in your own app. | Can support features like self-registration, password reset, and user lifecycle management (depending on the IdP). |
SSO login page | You define the Sign in URL and optionally the Sign out URL in the JWT configuration settings. | The login page is handled by the IdP, and redirects are managed through SAML/OpenID settings. |
Advanced features | Some features are not supported with JWT, such as:– Auto-register SSO readers– Skipping Document360's common sign-in page– Reader self-registration | These advanced features are available depending on the IdP’s capabilities. |
Implementation | Simpler setup for developers. You generate the JWT, sign it using a client secret created in Document360, and handle authentication in your app. | Requires configuration of IdP metadata, certificates, and mappings with Document360. |
Configuring JWT in Document360
Before implementing JWT SSO, you must first configure the JWT in Document360 and obtain the necessary credentials.
Creating a JWT
To create a JSON Web Token (JWT),
Log in to the Document360 portal.
Go to Settings ()> Users & permissions > JWT.
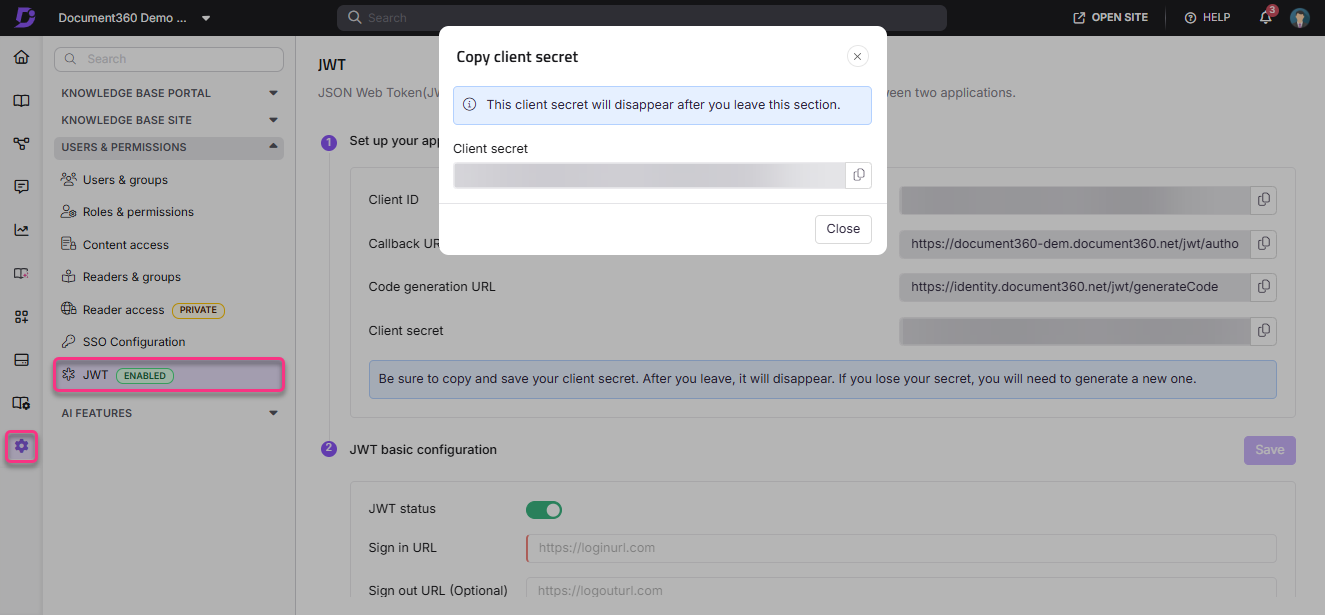
Create a JWT (Client secret) from here by clicking on the Create JWT button.
Copy the generated client secret by clicking on the copy icon and clicking on Close.
NOTE
The same generated Client secret will not be available when you revisit this section. If required, the client's secret must be regenerated.
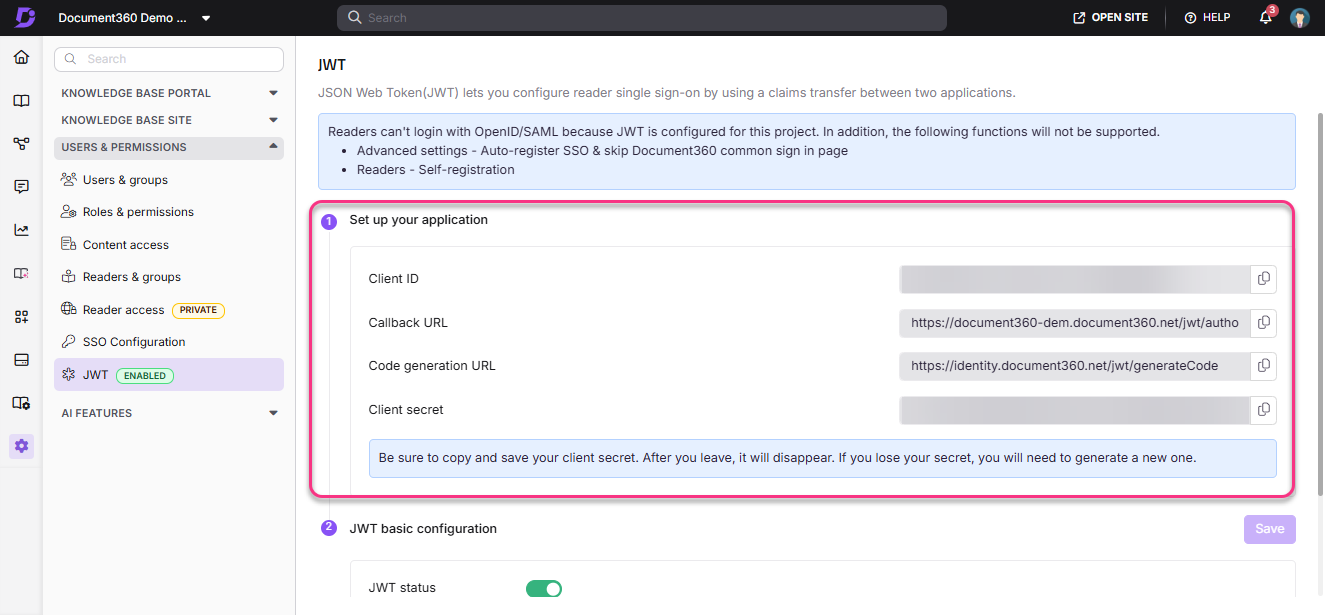
The JWT configuration page with all the data is now available.
JWT configuration page overview
After a JWT is created, the JWT configuration page will be visible.
Set up your application: Copy the Client ID, Callback URL, Code generation URL, Client secret, and paste them into the appropriate fields in the client application
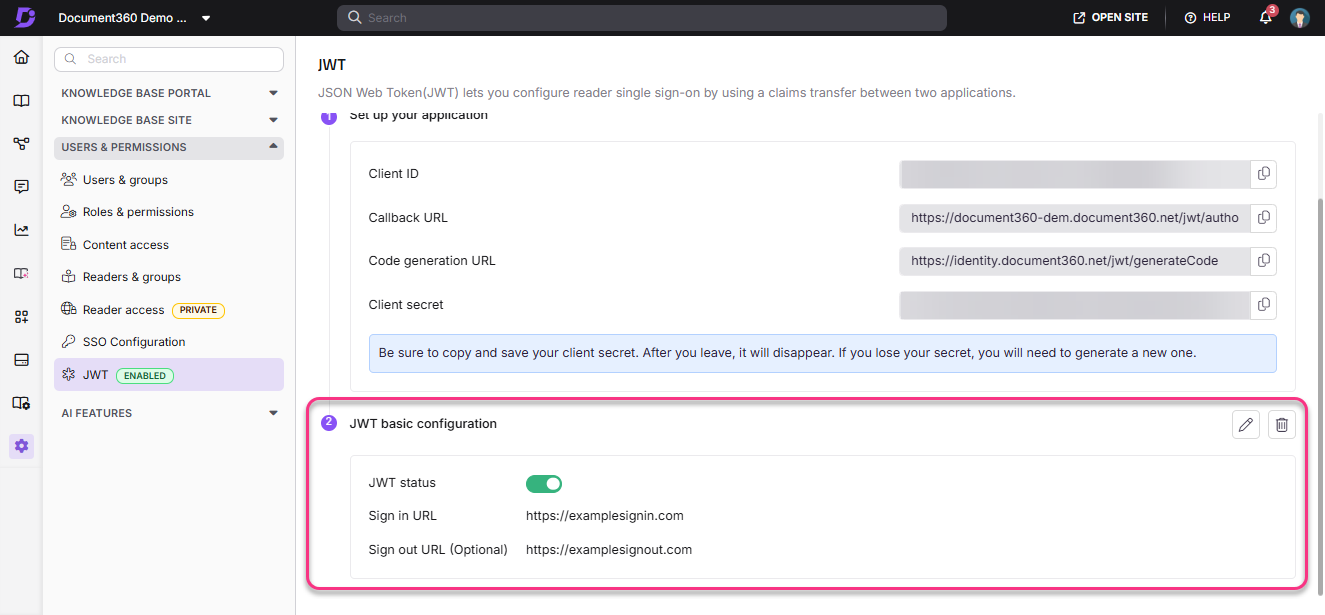
JWT status: Turn the JWT SSO login for readers on or off using this toggle. If the toggle is set to off, readers will not be able to log in to the knowledge base site using their client app credentials.
Delete JWT: Click the Delete button to remove the configured JWT. You cannot undo this action.
JWT basic configuration: Paste the login URL obtained from the client's application.
Readers will land on the dedicated logout page for JWT SSO readers if a custom logout link is not provided.
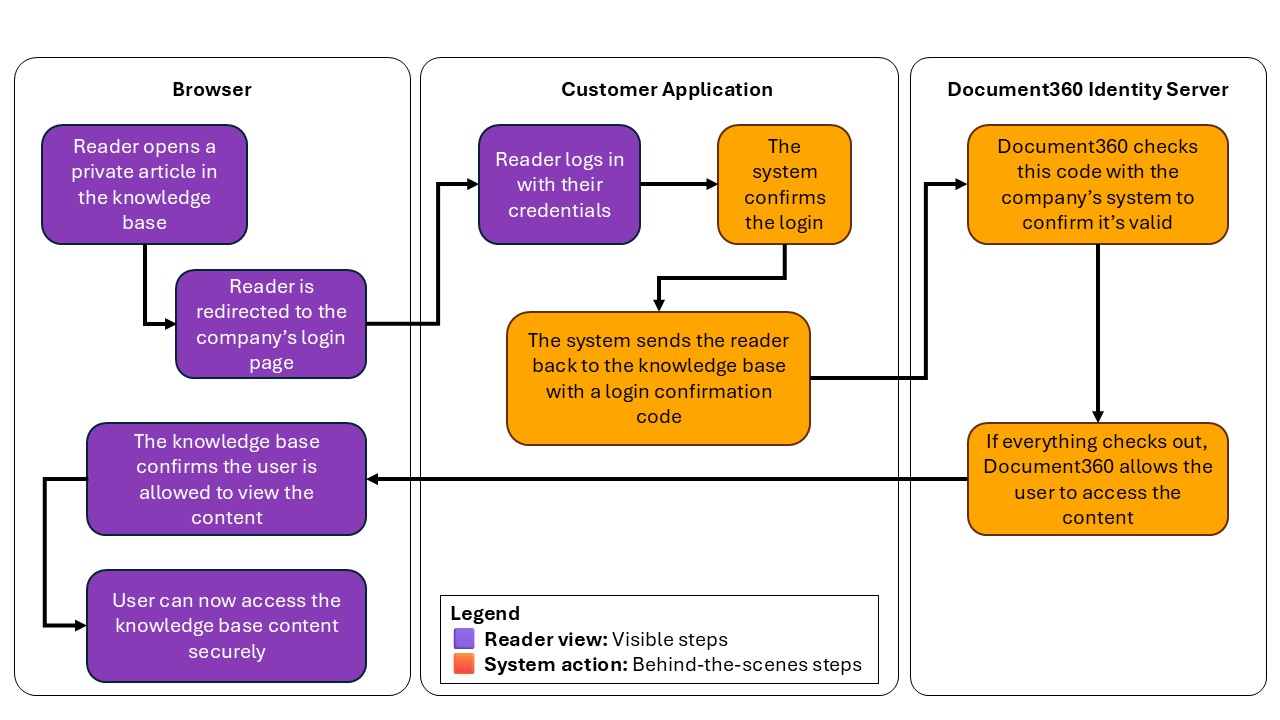
How JWT authentication works
The high-level diagram below shows how to achieve JWT authentication flow in Document360.
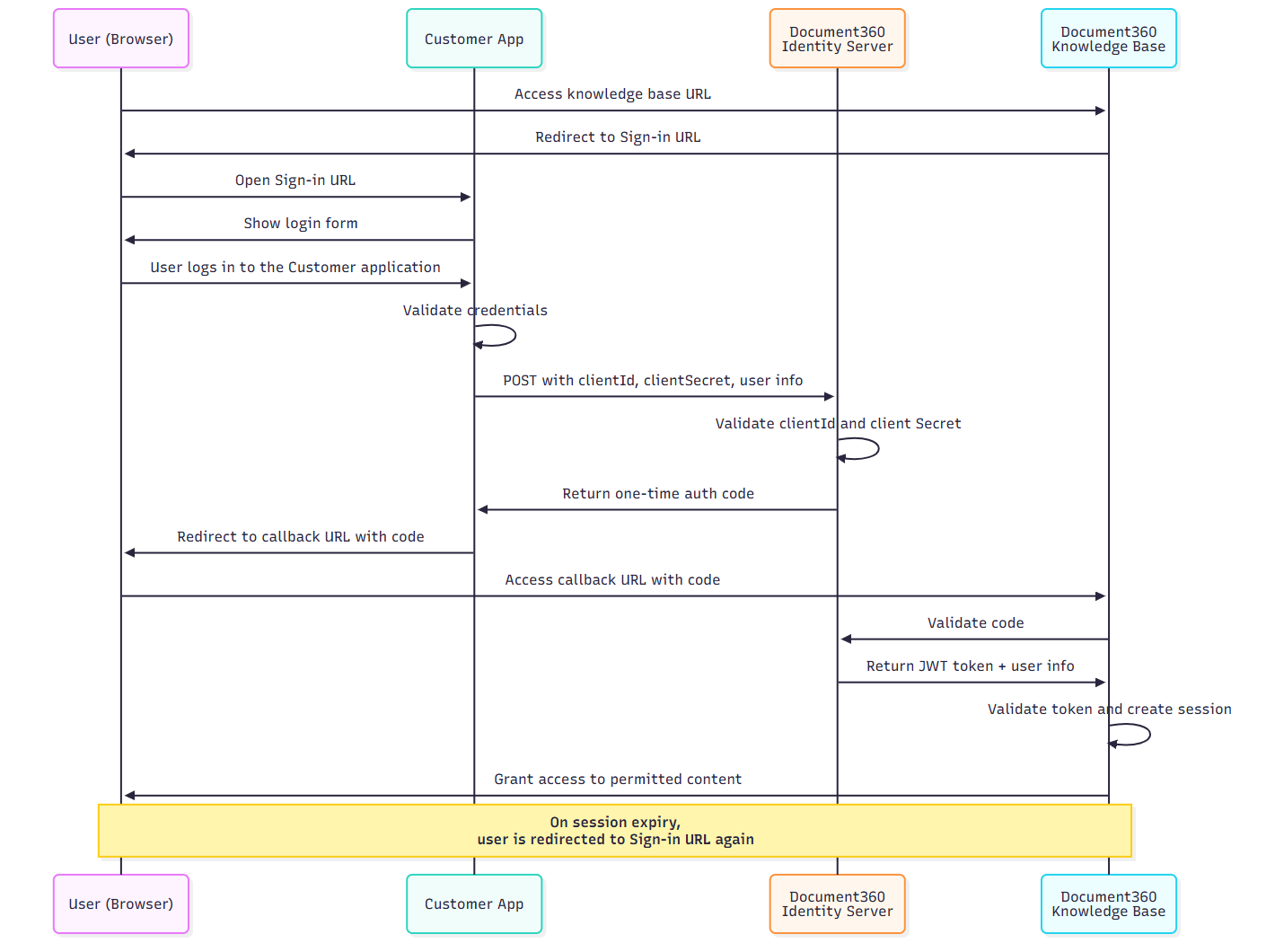
The steps below explain the complete JWT authentication flow in Document360 for developers setting up reader SSO using their own login system.
Key terminology
Term | Description |
|---|---|
Sign in URL | A public login page in your application where users are redirected to authenticate. |
Code generation URL | Secure backend endpoint in your app that sends user data to Document360 to obtain an authorization code. |
Callback URL | The URL in Document360 where your app redirects the user after receiving the authorization code. This is auto-generated by Document360. |
User accesses the private knowledge base
When a user tries to access your knowledge base site, Document360 detects that JWT SSO is enabled and redirects the user to the Sign in URL configured in JWT settings.
User logs in to your application
If the user is not already authenticated, your login page handles their authentication.
Your backend requests a one-time auth code
After the user logs in, your backend sends a
POSTrequest to the Code generation URL configured in Document360 with the following:User identity (e.g., name, email)
Optional
readerGroupIdstokenValidityin minutes
This request must be authorized using HTTP Basic Auth with your Client ID and Client Secret.
Example Authorization Header
Authorization: Basic Base64Encode(clientId:clientSecret)JSON Payload Example
{
"username": "firstname + lastname",
"firstName": "firstname",
"lastName": "lastname",
"emailId": "user email",
"readerGroupIds": ["Obtain from Reader groups overview page in the Document360 portal (Optional)"],
"tokenValidity": 15 //minutes
}NOTE
Ensure correct JSON syntax to avoid configuration errors.
Document360 Identity server returns an auth code
If the request is valid, Document360’s identity server generates a single-use authorization code and sends it back to your app (backend).
Your app redirects the user back to Document360
Your backend appends the code to the Callback URL and redirects the user to it.
For example:
https://yourproject.document360.io/jwt/authorize?code=xyz
NOTE
The authentication code is a one-time use code and cannot be reused.
Document360 validates the code
Once it receives the code, Document360 sends it to the identity server via backchannel to exchange it for a JWT token.
Reader session is created
Document360 extracts user information and access rules (based on
readerGroupIds) from the token.A session is created for the reader, granting them access to allowed categories, languages, or versions.
Token validity and session behavior
You can define the session duration using the
tokenValidityfield in the payload (min: 5 minutes, max: 1440).Once the token expires:
The reader is redirected back to your Sign in URL.
If the user is still authenticated in your app, a new code is generated, and the session is re-established seamlessly.
Developer checklist
Configure Sign in URL, Callback URL, and Code generation URL in JWT settings.
Generate and securely store your Client Secret (shown only once).
Set up backend logic to call the Code generation URL with Basic Auth.
Validate and sign the JWT securely in your backend.
Use HTTPS for all endpoints.
Test session behavior, expiration, and auto-renewal.
Monitor for 401 errors due to expired codes or token issues.
Implementing the JWT SSO redirect logic
After completing the JWT configuration in Document360, your application needs a backend route to handle the final step of the login flow.
This route:
Validates that the user is already authenticated in your application
Sends a secure request to Document360’s Code generation URL
Retrieves a one-time authorization code
Redirects the user to the knowledge base site with that code
/// <summary>
/// Example endpoint to authenticate a user and retrieve a token from the identity server,
/// and redirect the user to the Knowledge Base (KB) using the token code.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="clientId">Client ID issued for your application</param>
/// <param name="clientSecret">Client secret associated with the client ID</param>
/// <returns>Redirects to the KB with the issued code</returns>
[HttpGet]
[Route("authenticate")]
public async Task<IActionResult> AuthenticateAsync(string clientId, string clientSecret)
{
if (!HttpContext.User.Identity.IsAuthenticated)
{
// user is not authenticated, redirect to an error or login page
return Unauthorized(new { message = "User not authenticated" });
}
// Ensure you have the correct client ID and secret from your Document360 JWT configuration
var authToken = Encoding.ASCII.GetBytes($"{clientId}:{clientSecret}");
// Create an HttpClient instance
using var httpClient = new HttpClient();
// Set the Authorization header with Basic authentication
httpClient.DefaultRequestHeaders.Authorization = new AuthenticationHeaderValue("Basic", Convert.ToBase64String(authToken));
// Prepare the payload with user information
var payload = new
{
username = User.Identity.Name,
firstName = "FirstName", // Replace or customize as needed
lastName = "LastName",
emailId = "user@example.com", // Replace with actual user email
readerGroupIds = new List<string> { "group1", "group2" }, // Replace with actual reader group IDs if needed (Optional)
tokenValidity = 3600 // Token validity in seconds (Optional, default is 5 minutes)
};
var payloadContent = new StringContent(JsonConvert.SerializeObject(payload), Encoding.UTF8, "application/json");
// Identity server token endpoint - replace with your actual URL
string identityServerUrl = "codeGeneration endpoint, you can find that in JWT config portal";
// KB login URL to redirect after successful token issuance
string kbLoginUrl = "https://{your subdomain}.document360.io";
var response = await httpClient.PostAsync(identityServerUrl, payloadContent);
if (response.IsSuccessStatusCode)
{
var content = await response.Content.ReadAsStringAsync();
var tokenJson = JObject.Parse(content);
// Extract the code from the response
var tokenCode = (string)tokenJson.SelectToken("code");
// Construct the KB login URL with code query parameter
string finalRedirectUrl = $"{kbLoginUrl}?code={tokenCode}";
return Redirect(finalRedirectUrl);
}
else
{
// Handle error response from the identity server
var error = await response.Content.ReadAsStringAsync();
return StatusCode((int)response.StatusCode, new { error = "Token request failed", details = error });
}
}const express = require('express');
const https = require('https');
const axios = require('axios');
const app = express();
// Middleware to parse JSON
app.use(express.json());
// Replace with your actual client ID and secret from Document360
const clientId = 'b20bf794-050c-4194-bc30-bd834c51adad';
const clientSecret = '07U7nXLbOY7-klsmWrOOT3_qHa631XMOuqSd_gl69I8';
const codeGenerationUrl = 'https://identity.document360.net/jwt/generateCode';
// Your D360 KB URL (Replace your-subdomain)
const kbLoginUrl = 'https://jwt-readergroup1-sep.document360.net/jwt/authorize';
// ROUTE: /authenticate
app.get('/authenticate', async (req, res) => {
try {
// Example — add your real auth logic
const isAuthenticated = true;
if (!isAuthenticated) {
return res.status(401).json({ message: 'User not authenticated' });
}
// Basic Authorization header
const authHeader = Buffer.from(`${clientId}:${clientSecret}`).toString('base64');
// Payload to send to D360
const payload = {
username: 'john.doe',
firstName: 'John',
lastName: 'Doe',
emailId: 'john.doe@example.com',
readerGroupIds: ['group1', 'group2'],
tokenValidity: 3600
};
// POST to D360 identity server to get the code
const response = await axios.post(
codeGenerateUrl,
payload,
{
headers: {
'Authorization': `Basic ${authHeader}`,
'Content-Type': 'application/json',
'Accept': 'application/json'
},
httpsAgent: new https.Agent({ maxVersion: 'TLSv1.2' })
}
);
const tokenCode = response.data?.code;
if (!tokenCode) {
return res.status(500).json({ message: 'No code received from Document360' });
}
console.log("Redirecting to:", `${kbLoginUrl}?code=${tokenCode}`);
// Redirect user to KB with ?code=<token>
return res.redirect(`${kbLoginUrl}?code=${tokenCode}`);
} catch (error) {
console.error("JWT SSO error:", error.message);
return res.status(500).json({
message: "JWT SSO failed",
details: error.response?.data || error.message
});
}
});import org.springframework.http.*;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
import org.springframework.web.client.RestTemplate;
import org.springframework.web.util.UriComponentsBuilder;
import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;
import java.util.*;
@RestController
public class JwtSsoController {
private final String clientId = "your-client-id";
private final String clientSecret = "your-client-secret";
private final String codeGenerationUrl = "https://identity.document360.io/api/jwt/generate-code";
private final String kbLoginUrl = "https://your-subdomain.document360.io/jwt/authorize";
@GetMapping("/authenticate")
public ResponseEntity<?> authenticate() {
// Example: Check if user is authenticated in your system
boolean isAuthenticated = true; // Replace with actual logic
if (!isAuthenticated) {
return ResponseEntity.status(HttpStatus.UNAUTHORIZED).body("User not authenticated");
}
// Create Basic Auth header
String auth = clientId + ":" + clientSecret;
String encodedAuth = Base64.getEncoder().encodeToString(auth.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
HttpHeaders headers = new HttpHeaders();
headers.setContentType(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON);
headers.set("Authorization", "Basic " + encodedAuth);
headers.setAccept(Collections.singletonList(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON));
// Construct payload
Map<String, Object> payload = new HashMap<>();
payload.put("username", "john.doe");
payload.put("firstName", "John");
payload.put("lastName", "Doe");
payload.put("emailId", "john.doe@example.com");
payload.put("readerGroupIds", Arrays.asList("group1", "group2"));
payload.put("tokenValidity", 3600); // Optional
HttpEntity<Map<String, Object>> request = new HttpEntity<>(payload, headers);
RestTemplate restTemplate = new RestTemplate();
try {
ResponseEntity<Map> response = restTemplate.postForEntity(codeGenerationUrl, request, Map.class);
if (response.getStatusCode() == HttpStatus.OK && response.getBody() != null) {
String tokenCode = (String) response.getBody().get("code");
if (tokenCode == null || tokenCode.isEmpty()) {
return ResponseEntity.status(HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR)
.body("No code returned from Document360");
}
// Redirect to the KB site with code
String redirectUrl = UriComponentsBuilder.fromHttpUrl(kbLoginUrl)
.queryParam("code", tokenCode)
.toUriString();
HttpHeaders redirectHeaders = new HttpHeaders();
redirectHeaders.setLocation(java.net.URI.create(redirectUrl));
return new ResponseEntity<>(redirectHeaders, HttpStatus.FOUND); // 302 redirect
} else {
return ResponseEntity.status(HttpStatus.BAD_GATEWAY)
.body("Failed to get code from Document360: " + response.getStatusCode());
}
} catch (Exception ex) {
return ResponseEntity.status(HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR)
.body("JWT SSO error: " + ex.getMessage());
}
}
}Testing your JWT configuration
Once you've implemented the JWT SSO logic in your backend, you can test the integration using either cURL or Postman. These tests simulate how your backend communicates with the Document360 identity server to retrieve a one-time authorization code.
Testing JWT configuration using cURL
To test the JWT configuration, you can use the cURL command with the following specifications. The HTTP version should be specified (HTTP2 over TLS and version of SSL to TLS 1.2. Without this, the cURL would fail.
curl -X POST https://identity.document360.io/api/jwt/generate-code \
-H "Authorization: Basic BASE64_ENCODED_CLIENTID:CLIENTSECRET" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
--http2-prior-knowledge \
--tls-max 1.2 \
-d '{
"username": "john.doe",
"firstName": "John",
"lastName": "Doe",
"emailId": "john.doe@example.com",
"readerGroupIds": ["group1", "group2"],
"tokenValidity": 15
}'
NOTE
Replace the encoded authorization string and payload fields with your actual client credentials and user information from your system.
Unlike other IdP options available (Okta, Azure AD, etc.), the user does not need a separate reader account on Document360. An account on the client application is sufficient.
After enabling the JWT login, the reader can use the client application to log in as a reader account on the Document360 knowledge base site.
NOTE
Currently, Document360 provides an either-or functionality for the SSO standards. Once the IdP is configured using an SSO standard (SAML, OpenID or JWT) for a project, the user cannot create another simultaneous session.
For example, if a project is configured in the OpenID standard with Okta as IdP, the SAML and the JWT options would be deactivated.
Testing JWT configuration using Postman
You can test your JWT SSO configuration using Postman by manually sending a request to the Code generation URL. This allows you to verify that your client credentials and payload are accepted and that a one-time authorization code is generated successfully.
To test using Postman, follow these steps:
Open Postman and create a new request.
Set the request method to POST, and in the URL field, enter the Code generation URL from the JWT configuration screen:
https://identity.document360.io/api/jwt/generate-codeGo to the Authorization tab.
Set the Type to
Basic Auth.In the Username field, enter your Client ID.
In the Password field, enter your Client Secret.
Navigate to the Body tab.
Select the raw option and set the format to JSON.
Enter the required JSON payload. Example:
{ "username": "john.doe", "firstName": "John", "lastName": "Doe", "emailId": "john.doe@example.com", "readerGroupIds": ["group1", "group2"], "tokenValidity": 15 }Click Send to submit the request.
If the configuration is correct, you should receive a 200 OK response with a one-time code. You can then use this code to redirect the reader to the knowledge base site and complete the SSO login flow.
Redirection to other pages instead of the home page
By default, after logging in, users are redirected to the Home page of your knowledge base.
If your Home page is unpublished, users will be redirected to the /docs page.
To redirect users to a different page in your knowledge base (other than the Home or /docs pages), configure the redirection during JWT setup using the following code.
URL pattern
https://<Knowledge base URL>/jwt/authorize?code=<code>&redirectUrl=<redirect path>Parameters
<Knowledge base URL>: The main URL of your knowledge base site.
<Code>: The client ID.
<redirect path>: The new URL where you want users to land after login.
Example
https://example.document360.io/jwt/authorize?code=FOTaS_SW6dLGytQXvrG_rRFGhyPvrDDrgxJAZzYvJcY&redirectUrl=/docs/5-basic-things-to-get-started
NOTE
Document360 will send the Redirection URL as
redirectPathto the login endpoint. When the login endpoint redirects back to the knowledge base with the authentication code, it should return the Redirection URL as aredirectUrlparameter.In KB Site 2.0, redirection is handled using cookies instead of the
redirectUrlparameter. If your JWT implementation is based on query string redirection (using theredirectUrlparameter), please note that the cookie-based approach does not support this parameter. You may need to update your implementation or contact support for further clarification.
Troubleshooting
If you encounter issues during the JWT SSO setup, refer to the following common errors and their solutions:
401-unauthorized error when testing JWT in Postman
Error: 401 Unauthorized error
If you encounter a 401 Unauthorized error while testing JWT (JSON Web Token) using Postman, this typically occurs because the authorization settings are not configured correctly.
Steps to resolve:
To resolve this error,
In Postman, open the request you are testing.
Navigate to the Authorization tab.
Set the authorization type to Basic Auth.
In the Username field, enter the Client ID.
In the Password field, enter the Client Secret.
Go to the Body tab.
Select the raw option from the dropdown and ensure the format is set to JSON.
Add the required JSON payload for the API request.
Click Send to execute the request.
Check the response for the expected results. If the request is successful, you should receive an auth code or token in the response.
FAQ
Can I use a single JWT login to support multiple instances of my application on the same Document360 Knowledge base site?
No, currently, Document360 supports a single JWT login configuration per project.
A common JWT login cannot be shared across multiple instances of your application for the same Document360 knowledge base.
Each project can only authenticate one JWT application instance at a time.
If a configured JWT user logs out of the client application, does that mean they would also be logged out of Document360?
No, the session on Document360 is independent after the initial Single Sign-On. Users can continue using Document360 until the token's validity expires, even after logging out of the client application.
Example: If the token validity is set to 1 day, the Document360 session will remain active until the token expires. Once it does, the user will be logged out.
What are the minimum and the maximum token validity bands?
The minimum value that can be set is 5 minutes, and the maximum value that can be set is 1440 minutes (1 day).
Can I provide a value that exceeds the allowed token validity band?
No, if a value outside the range is provided, the system will automatically assign the nearest allowed value:
5 minutes for values below the minimum.
1440 minutes for values above the maximum.
What is the difference between JWT and SSO?
You can view a comparison between JWT (JSON Web Token) and SSO (Single Sign-On) in the table below:
Category | JWT (JSON Web Token) | SSO (Single Sign-On) |
Authentication | Tokens generated per session/user request. | Centralized authentication across apps. |
Token Expiry | Tokens typically expire after a set period. | No token, session handled by identity provider. |
Security | Requires secure token storage. | More secure, centralized credential storage. |
Usage | Used for stateless, single-use authentication. | Used for multiple applications with a single login. |
Integration | Easier to implement in custom apps. | Requires integration with an identity provider. |
Can readers log in with OpenID or SAML if JWT is configured for the project?
No, readers cannot log in with OpenID or SAML if JWT is configured for the project. Document360 allows only one SSO standard (JWT, OpenID, or SAML) to be active per project at a time.
What features are not supported when JWT is configured for the project?
The following functions are not supported when JWT is configured for the project:
Advanced Settings: Auto-register SSO and skip the Document360 common sign-in page.
Readers: Self-registration.
Will our JWT setup or user access change after migrating to the KB site 2.0?
No. When you migrate to KB site 2.0, there will be no changes to your current JWT configuration, reader access, or internal users. A dedicated migration team will support you through the process, ensuring that your existing customizations and settings remain intact after your review.
How can I ensure that JWT-related activities are captured in audit logs?
To track JWT activities, make sure your audit settings are configured correctly.
To enable JWT activity tracking:
In the Knowledge base portal, go to Settings () > Knowledge base portal > Team auditing.
Go to the Audit configuration tab, and ensure the following toggles are enabled:
JWT created
JWT saved
JWT deleted!
JWT generated
JWT updated
Once enabled, navigate to the Team auditing tab.
All JWT-related activities will be recorded here from that point onwards.NOTE
For easier navigation, use the Event dropdown to filter JWT activities. Type JWT in the search bar, select the desired event(s), and click Apply to view relevant audit records.