Plans supporting this feature: Professional Business Enterprise
What is a Robots.txt file?
A Robots.txt file is a text file used to communicate with web crawlers and other automated agents about which pages of your knowledge base should not be indexed. It contains rules specifying which pages may be accessed by which crawlers.
NOTE
For more information, read this help article from Google.
Accessing Robots.txt in Document360
To access Robots.txt in Document360:
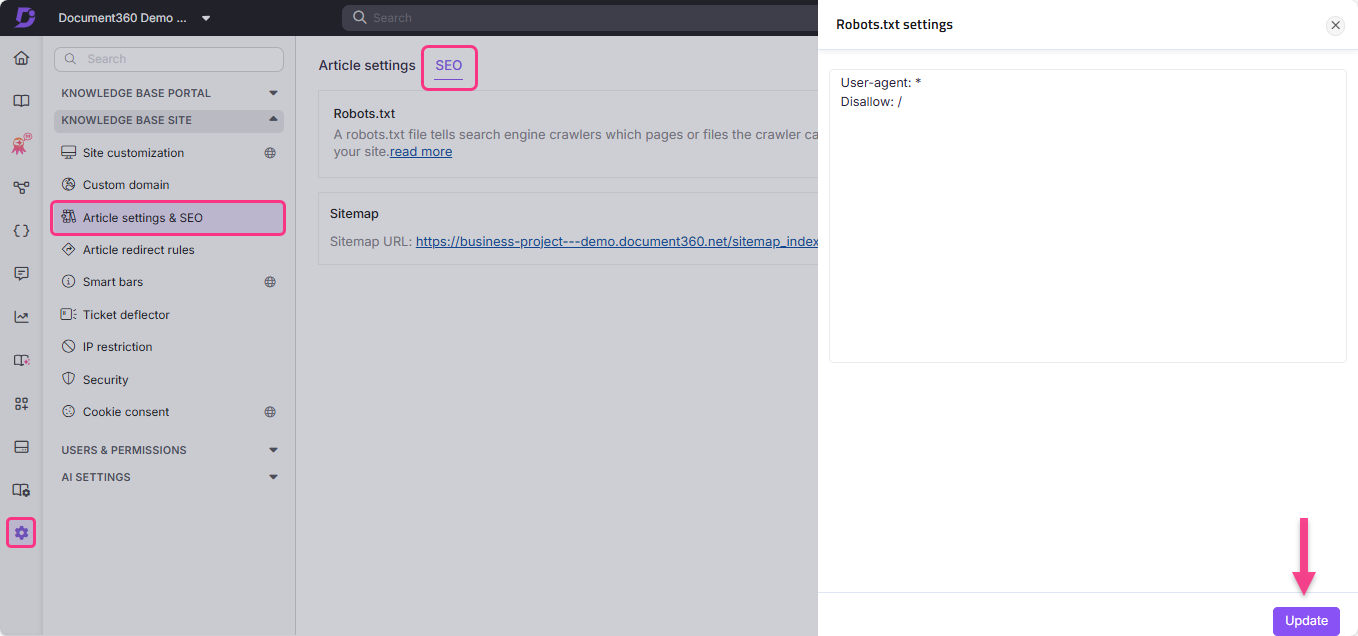
Navigate to Settings () in the left navigation bar
Go to Knowledge base site > Article settings & SEO > SEO tab.
Locate Robots.txt and click Edit.
The Robots.txt settings panel will appear.
Type in your desired rules.
Click Update.
Use cases of Robots.txt
A Robots.txt file can block a folder, file (such as a PDF), or specific file extensions from being crawled.
You can also delay the crawl speed of bots by adding crawl-delay in your Robots.txt file. This is useful when your site is experiencing high traffic.
User-agent: *
Crawl-delay: 10Restricting the crawler through admin data
User-agent: *
Disallow: /admin/
Sitemap: https://example.com/sitemap.xml
User-agent: * - Specifies that any bot can crawl through the site.Disallow: /admin/: - Restricts the crawler from accessing admin data.Sitemap: https://example.com/sitemap.xml - Provides access to bots to crawl the sitemap. This makes the crawl easier as the sitemap contains all the URLs of the site.
Restricting a specific search engine from crawling
User-agent: Bingbot
Disallow: /
The above Robots.txt file is defined to disallow the Bingbot.
User-agent: Bingbot - Specifies the crawler from the Bing search engine.Disallow: / - Restricts Bingbot from crawling the site.
Best Practices
Include links to the most important pages.
Block links to pages that do not provide any value.
Add the sitemap location in the Robots.txt file.
A Robots.txt file cannot be added twice. Please check the basic guidelines from Google Search Central documentation for more information.
NOTE
A web crawler, also known as a Spider or Spiderbot, is a program or script that automatically navigates the web and collects information about various websites. Search engines like Google, Bing, and Yandex use crawlers to replicate a site's information on their servers.
Crawlers open new tabs and scroll through website content, just like a user viewing a webpage. Additionally, crawlers collect data or metadata from the website and other entities (such as links on a page, broken links, sitemaps, and HTML code) and send it to the servers of their respective search engine. Search engines use this recorded information to index search results effectively.
FAQs
How do I remove my Document360 project from the Google search index?
To exclude the entire project from the Google search index:
Navigate to Settings () in the left navigation bar in the Knowledge base portal.
In the left navigation pane, navigate to Knowledge base site > Article settings & SEO > SEO tab.
Go to the SEO tab and click Edit in the
Robots.txt.Paste the following code:
User-Agent: Googlebot
Disallow: Click Update.
How do I prevent tag pages from being indexed by search engines?
To exclude the tag pages from the search engines:
Navigate to Settings () in the left navigation bar.
Go to Knowledge base site > Article settings & SEO > SEO tab.
Click Edit in the
Robots.txt.Paste the following code:
User-agent: *
Disallow: /docs/en/tags/Click Update.